How your sleeping position affects your health
by admin
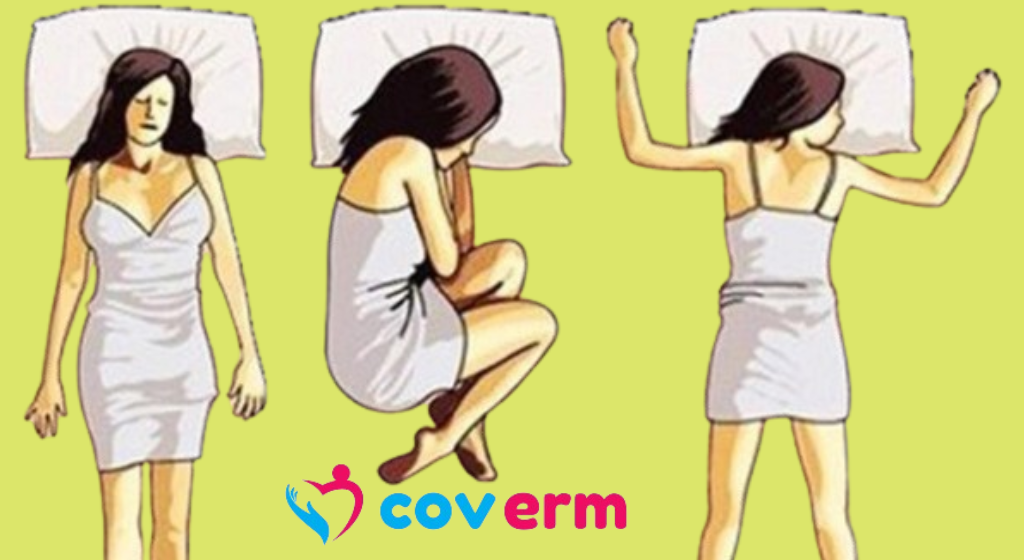
Choosing the best sleeping position depends on various factors such as comfort, health conditions, and personal preferences. Here’s a breakdown of the most common sleeping positions and their effects on the body:
- Fetal Position:
- Benefits: Allows the spine to rest in a natural position, may reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease, ideal for pregnant women.
- Considerations: May cause pressure on the lungs and diaphragm.
- Side Sleeping (Type Position):
- Benefits: Reduces sleep apnea, relieves neck and back pain.
- Recommendation: Place a soft pillow between your knees to reduce pressure on the pelvic area.
- Free Fall Position (Stomach Sleeping):
- Considerations: Not considered healthy, may cause back and neck pain.
- Recommendations: Use a soft pillow that doesn’t elevate the neck too much, place a thin pillow under the forehead to keep the airway open.
- Soldier’s Pose (Back Sleeping):
- Considerations: May lead to snoring and carotid artery issues.
- Recommendations: Place a small pillow under the knee area to support the spine and reduce back pain.
Important Factors Affecting Sleeping Position:
- Back and Neck Pain: Consider using pillows strategically to support the spine and alleviate pressure points.
- Snoring and Sleep Apnea: Side or stomach sleeping may help alleviate snoring and sleep apnea symptoms.
- Heartburn and Acid Reflux: Sleeping on the left side may help reduce symptoms of heartburn and acid reflux compared to sleeping on the right side.
Ultimately, the best sleeping position varies from person to person, so it’s essential to consider individual comfort and any specific health concerns when choosing a sleeping position. Experimenting with different positions and pillow arrangements may help identify the most comfortable and beneficial sleeping position for each individual.