7 signs of ovarian cancer that can be easily missed
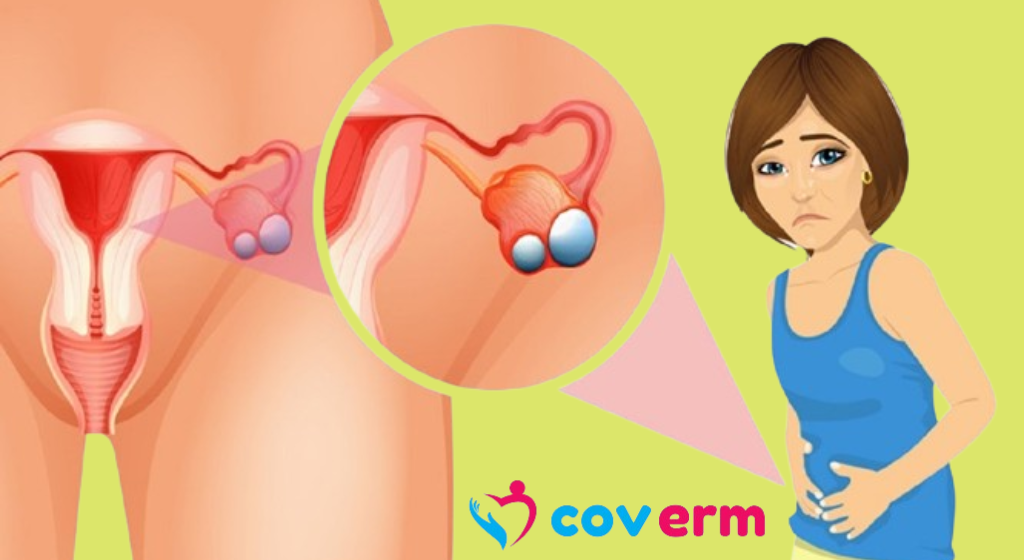
Ovarian cancer originates from the rapid multiplication of cells within the ovaries, which can infiltrate and damage healthy tissues.
Located on each side of the uterus, the female reproductive system houses two ovaries, each approximately the size of an almond, responsible for egg production and hormone secretion, including estrogen and progesterone.
Symptoms: Ovarian cancer may commence without noticeable symptoms, often resembling other common conditions. However, when symptoms do emerge, they might include:
- Abdominal bloating or swelling
- Early satiety during meals
- Unexplained weight loss
- Pelvic discomfort
- Fatigue
- Back pain
- Changes in bowel habits, such as constipation
- Increased urinary frequency
When to Seek Medical Attention: If you experience any concerning signs or symptoms, consult a healthcare professional.
Causes:
The exact causes of ovarian cancer remain unclear, although certain factors can heighten the risk:
- Aging: Ovarian cancer becomes more prevalent with advancing age.
- Inherited Genetic Mutations: Specific gene mutations, such as BRCA1 and BRCA2, inherited from parents, can increase susceptibility to ovarian cancer.
- Family History: A family history of ovarian cancer elevates the risk of developing the disease.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is associated with a higher risk of ovarian cancer.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Postmenopausal hormone replacement therapy may elevate ovarian cancer risk.
- Endometriosis: This condition, characterized by uterine lining tissue growing outside the uterus, is linked to a heightened risk of ovarian cancer.
- Menstrual Factors: Starting menstruation at an early age or experiencing menopause later in life can increase ovarian cancer risk.
- Nulliparity: Never having been pregnant may contribute to a higher risk of ovarian cancer.
Prevention: While there’s no guaranteed method for preventing ovarian cancer, certain strategies may help reduce risk:
- Birth Control Pills: Consider discussing oral contraceptive use with your doctor, as it has been associated with a reduced risk of ovarian cancer.
- Genetic Counseling: Inform your doctor about any family history of breast or ovarian cancer, as this may prompt genetic testing and counseling. Depending on the results, preventive measures like oophorectomy (ovary removal) may be considered.